Cyber Security Awareness – How to be Safe Online
In today’s digital age, the internet has become an integral part of our lives. It is hard to imagine a day without browsing the internet or using social media. However, with the increase in internet usage, cybersecurity threats have also grown. Cybercriminals are always looking for ways to steal sensitive information and cause damage to individuals and businesses. Therefore, it is essential to be aware of cybersecurity risks and take necessary measures to protect yourself.
There are various ways in which a person or organization can get hacked. Here are some common methods that hackers use and how you can stay safe:
Email Phishing
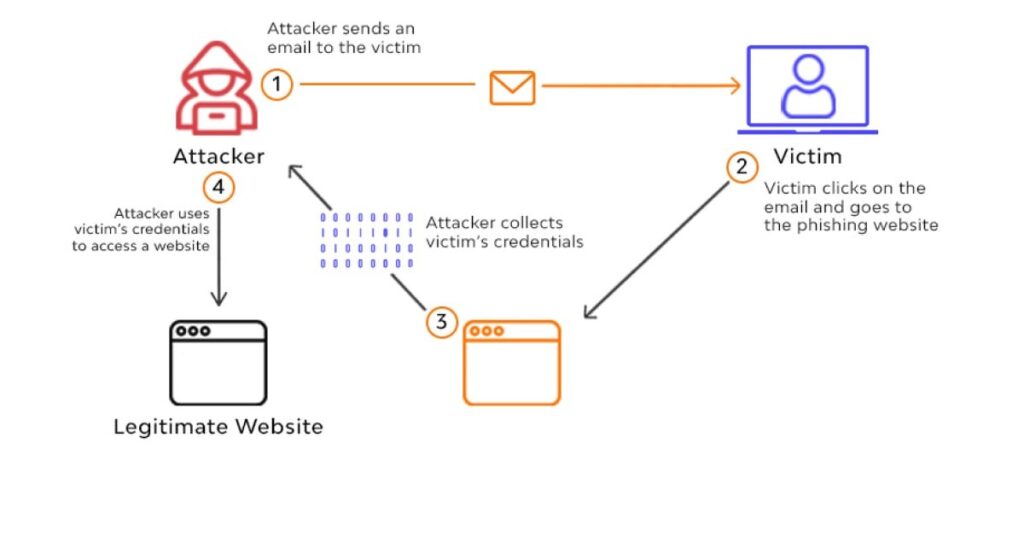
Email phishing is a type of cyber attack in which an attacker sends a fraudulent email that appears to be from a legitimate source, such as a bank, social media platform, or email provider. The goal of the attacker is to trick the recipient into providing sensitive information, such as login credentials, financial information, or personal data.
Email phishing attacks often use tactics such as urgent requests, threats of account closure or suspension, or promises of rewards or incentives to entice the recipient to click on a link or download an attachment. These links and attachments may contain malware or lead to a fake website designed to steal sensitive information.
To protect yourself from email phishing attacks, there are several steps you can take:
- Verify the sender: Check the sender’s email address and verify that it is from a legitimate source. Be cautious of emails that come from suspicious or unfamiliar email addresses.
- Look for red flags: Be wary of emails that contain urgent requests, grammatical errors, or strange formatting. These can be signs of a phishing attack.
- Don’t click on links or download attachments: Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources. If you are unsure about an email, contact the sender directly to confirm its legitimacy.
- Use two-factor authentication: Use two-factor authentication whenever possible to add an extra layer of security to your accounts.
- Keep your software up to date: Keep your operating system, email client, and anti-virus software up to date to prevent vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
- Report suspicious emails: Report any suspicious emails to your email provider or IT department. This can help prevent further attacks and protect others from falling victim to the same scam.
Malware
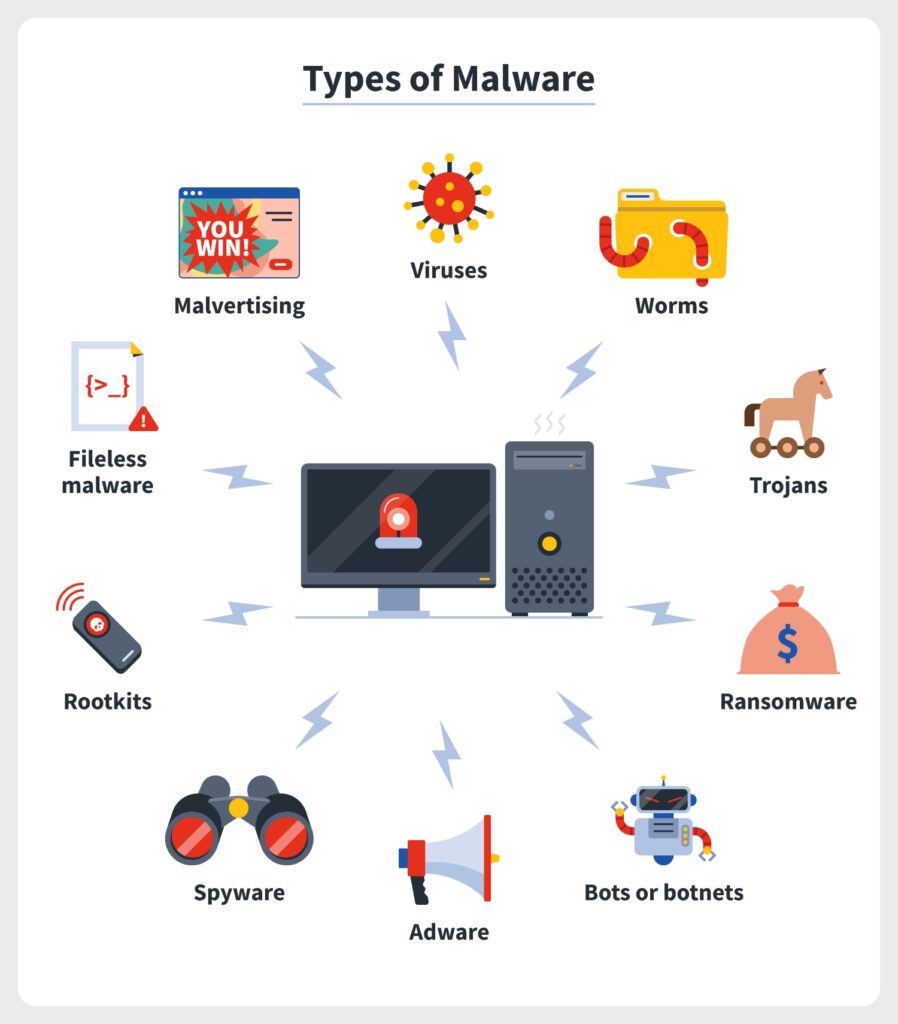
Malware is short for malicious software and refers to any type of software designed to harm, disrupt or exploit a computer system, network, or device. Malware is a serious threat to computer security, as it can steal sensitive information, damage files, and even take control of entire systems.
Here are some common types of malware:
- Viruses: A virus is a type of malware that can replicate itself and spread from one computer to another. Viruses can damage or destroy files, steal information, or cause other harmful effects.
- Worms: A worm is a type of malware that spreads through computer networks by exploiting vulnerabilities in software. Worms can cause a lot of damage by consuming system resources and slowing down networks.
- Trojan Horses: A Trojan horse is a type of malware that disguises itself as a legitimate program or file. Once installed, it can give an attacker remote access to the infected computer or steal sensitive information.
- Ransomware: Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts the victim’s files and demands payment in exchange for the decryption key. Ransomware attacks can cause significant damage and often result in financial losses.
- Spyware: Spyware is a type of malware that is designed to collect information about a user’s computer or network without their knowledge. This information can be used for various purposes, including identity theft, financial fraud, and espionage.
To protect yourself from malware, here are some tips:
- Use anti-virus software: Install and use reputable anti-virus software on your computer, and keep it up-to-date to ensure it can detect and block new threats.
- Keep your software up-to-date: Regularly update your operating system and software to fix known vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
- Be cautious of downloads: Only download software and files from trusted sources. Avoid downloading software from peer-to-peer networks, torrents, or other untrusted sources.
- Be wary of email attachments: Do not open email attachments from unknown senders or unexpected emails, and always scan attachments with anti-virus software before opening them.
- Backup your data: Regularly back up your data to an external hard drive or cloud storage service to protect against data loss from malware attacks.
Smishing
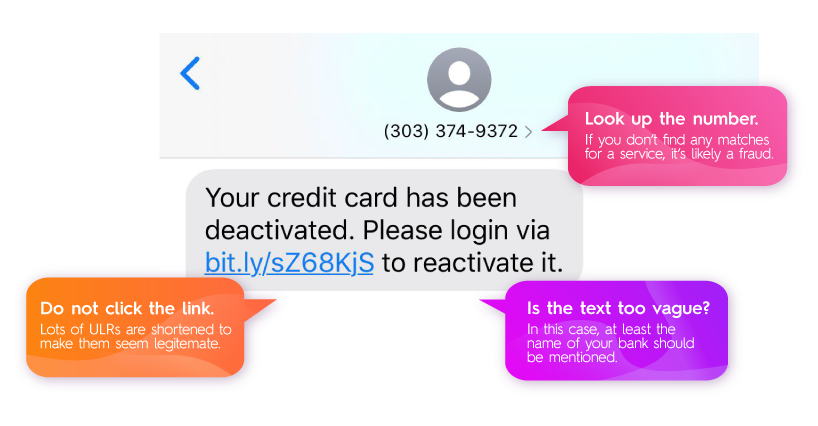
Smishing is a type of phishing attack that involves sending text messages (SMS) or multimedia messages (MMS) to mobile devices to trick the recipient into providing personal information or clicking on a malicious link. Smishing attacks are becoming increasingly common, as more people use mobile devices for online banking, shopping, and other sensitive activities.
Smishing attacks often use similar tactics to email phishing attacks, such as urgent requests, threats of account closure or suspension, or promises of rewards or incentives. The goal of the attacker is to trick the recipient into clicking on a link or providing sensitive information, which can then be used to steal money, identities, or other valuable information.
To protect yourself from smishing attacks, here are some tips:
- Be wary of unexpected messages: Be cautious of unexpected text messages, especially if they contain a sense of urgency or require you to take immediate action.
- Verify the sender: Check the sender’s phone number and verify that it is from a legitimate source. Be cautious of text messages that come from suspicious or unfamiliar phone numbers.
- Don’t click on links: Avoid clicking on links in text messages from unknown sources. If you are unsure about a message, contact the sender directly to confirm its legitimacy.
- Be cautious of offers or rewards: Be skeptical of text messages offering rewards or incentives, as these can be a common tactic used by smishing attackers to lure victims into providing sensitive information.
- Use two-factor authentication: Use two-factor authentication whenever possible to add an extra layer of security to your accounts.
- Keep your software up to date: Keep your mobile device’s operating system, apps, and anti-virus software up to date to prevent vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Vishing
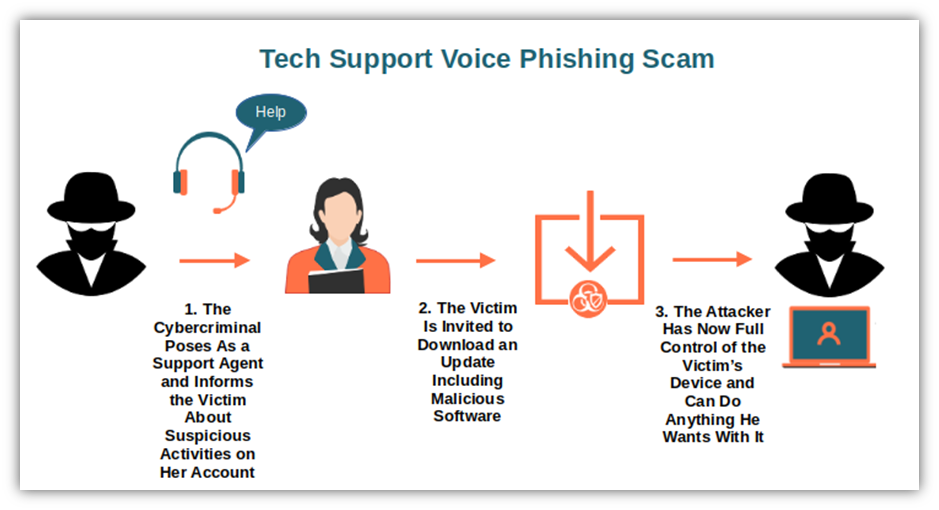
Vishing, or voice phishing, is a type of social engineering attack that uses phone calls to trick victims into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials, credit card numbers, or social security numbers. Vishing attacks can be especially effective because they create a sense of urgency or panic in the victim, making them more likely to divulge information.
Vishing attackers may use automated voice messages or call scripts to impersonate legitimate organizations, such as banks or government agencies, and request sensitive information from the victim. They may also use spoofing techniques to make it appear that the call is coming from a trusted source, such as a local phone number or the victim’s bank.
To protect yourself from vishing attacks, here are some tips:
- Verify the caller: Always verify the identity of the caller before providing any personal information. Ask for their name, department, and contact information, and then call the organization back using a trusted phone number to confirm their identity.
- Be wary of urgent requests: Be skeptical of urgent requests for personal information, especially if the caller is pressuring you to act quickly.
- Don’t give out personal information: Never give out personal information, such as passwords or credit card numbers, over the phone unless you are sure of the caller’s identity.
- Use two-factor authentication: Use two-factor authentication whenever possible to add an extra layer of security to your accounts.
- Be cautious of unsolicited calls: Be cautious of unsolicited calls, especially those from unknown numbers. If you receive a suspicious call, hang up and report it to the appropriate authorities.
- Educate yourself: Stay informed about the latest vishing tactics and how to protect yourself from these types of attacks.
Password Attacks
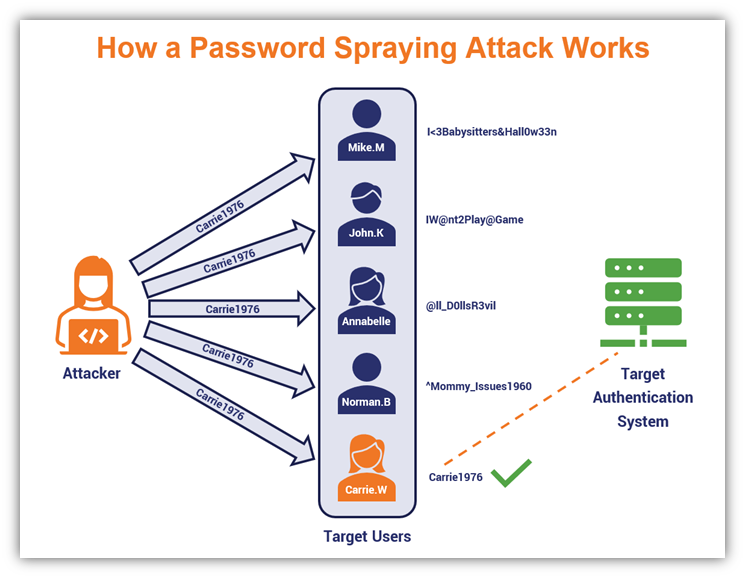
Password attacks are a common form of cyber attack in which an attacker attempts to gain unauthorized access to a victim’s accounts by guessing or stealing their passwords. Password attacks can take many forms, including brute-force attacks, dictionary attacks, and phishing attacks.
Brute-force attacks involve an attacker using a program to repeatedly guess passwords until they find the correct one. This type of attack can be time-consuming and is usually used when the attacker has no information about the victim’s password.
Dictionary attacks involve an attacker using a program to try a list of common passwords or words until they find the correct one. This type of attack is often successful because many people use common or easily guessable passwords.
Phishing attacks involve an attacker tricking the victim into revealing their password by posing as a legitimate organization or individual. This can be done through fake login pages, emails, or messages that appear to be from a trusted source.
To protect yourself from password attacks, here are some tips:
- Use strong passwords: Use long, complex passwords that include a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols preferably 16 digits. Avoid using common words or phrases that can be easily guessed.
- Use a password manager: Use a password manager to create and store strong, unique passwords for all your accounts.
- Enable two-factor authentication: Enable two-factor authentication whenever possible to add an extra layer of security to your accounts.
- Be wary of suspicious emails: Be cautious of suspicious emails or messages that ask for your password or other sensitive information. Don’t click on links or download attachments unless you are sure they are safe.
- Keep your software up to date: Keep your operating system, web browser, and other software up to date with the latest security patches to prevent vulnerabilities that could be exploited by password attacks.
- Educate yourself: Stay informed about the latest password attack tactics and how to protect yourself from them.
Unsecured Networks
An unsecured network is a network eg WiFi, that does not require a password or other form of authentication to access it. Unsecured networks can be found in public places such as coffee shops, airports, and hotels, as well as in private homes and businesses.
Connecting to an unsecured network can put your device and your personal information at risk. Here are some of the risks associated with unsecured networks:
- Man-in-the-middle attacks: An attacker can intercept the traffic between your device and the network and steal your personal information, such as login credentials or credit card numbers.
- Malware infections: An attacker can use the unsecured network to distribute malware to your device, which can be used to steal your personal information or damage your device.
- Unauthorized access: An attacker can use the unsecured network to gain unauthorized access to your device or the files and data on it.
To protect yourself from these risks, here are some tips:
- Avoid unsecured networks: Whenever possible, avoid connecting to unsecured networks. Use a trusted network with strong encryption, such as your home or work network, or a trusted public network that requires a password to access.
- Use a virtual private network (VPN): If you must connect to an unsecured network, use a VPN to encrypt your traffic and protect your personal information.
- Disable file sharing: Disable file sharing on your device when connecting to an unsecured network to prevent unauthorized access to your files and data.
- Keep your software up to date: Keep your operating system, web browser, and other software up to date with the latest security patches to prevent vulnerabilities that could be exploited on an unsecured network.
- Use a firewall: Use a firewall to monitor and control incoming and outgoing traffic on your device to prevent unauthorized access and protect against malware.
In conclusion, to be secure online, it’s important to follow some best practices, such as
- Use strong and unique passwords
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Avoid unsecured networks
- Keep software up to date
- Use antivirus software
- Be cautious of suspicious emails and messages
- Educate yourself on the latest threats and how to protect against them







